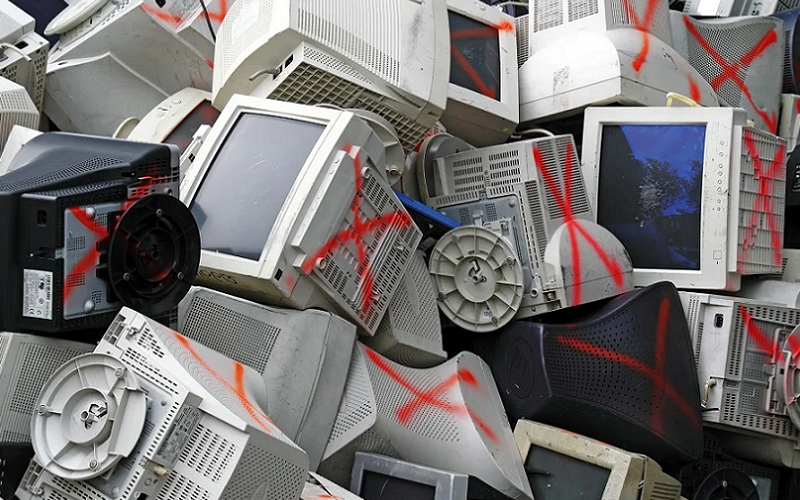

In recent years, the development of biodegradable electronics has been gaining traction in the field of technology. These new devices have the potential to revolutionize the way we think about electronics and their impact on the environment. Unlike traditional electronics, which often end up in landfills, biodegradable electronics are designed to break down naturally and safely.
What Are Biodegradable Electronics?
Biodegradable electronics are a new class of electronic devices that are designed to break down naturally and safely in the environment. Unlike traditional electronics, which often contain harmful chemicals and materials that can harm the environment and pose a risk to human health, biodegradable electronics are made from materials that are safe for the environment.
The development of biodegradable electronics is driven by the need to reduce electronic waste, which has become a significant environmental problem in recent years. Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a growing concern because it contains toxic chemicals and materials that can leach into the soil and water, contaminating the environment and posing a risk to human health. By creating biodegradable electronics, researchers and companies hope to reduce the amount of e-waste generated and promote a more sustainable future.
There are several different types of biodegradable electronics that are currently being developed. One approach is to use materials that can be broken down by natural processes, such as cellulose or silk. These materials can be used to create flexible electronic devices, such as wearable sensors or implantable medical devices, that can be safely absorbed by the body or broken down in the environment.
Another approach is to use materials that can be broken down by exposure to heat or light. For example, some researchers are exploring the use of polymer materials that can be triggered to break down when exposed to UV light or heat. These materials can be used to create electronic devices that can be safely disposed of by simply exposing them to sunlight or heat.
Despite the potential benefits of biodegradable electronics, there are also some challenges and limitations to their development. For example, biodegradable materials may not be as durable or long-lasting as traditional electronic materials, which can make them less practical for certain applications. There are regulatory and safety concerns that need to be addressed before biodegradable electronics can be widely used in consumer products.

Environmental Benefits of Biodegradable Electronics
Biodegradable electronics have the potential to provide several environmental benefits when compared to traditional electronics.
Biodegradable Electronics Reduce Electronic Waste
One of the most significant environmental benefits of biodegradable electronics is the reduction in electronic waste. Traditional electronic devices are made from materials that can take decades or even centuries to decompose, and they often end up in landfills, where they can leach toxic chemicals into the soil and water. In contrast, biodegradable electronics are designed to break down naturally and safely in the environment, which can help to reduce the amount of electronic waste generated.
Biodegradable Electronics Offer Safe Disposal
Biodegradable electronics can be safely disposed of without harming the environment. This is particularly important for electronic devices that are difficult to recycle, such as medical implants or wearable sensors. With biodegradable electronics, these devices can be safely absorbed by the body or broken down in the environment, reducing the need for special disposal methods.
Biodegradable Electronics Provide a Reduction in Carbon Footprint
The production of traditional electronic devices requires large amounts of energy and resources, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Biodegradable electronics, on the other hand, can be made from renewable resources and produced using less energy-intensive processes, which can help to reduce the carbon footprint of electronic devices.
Biodegradable Electronics Have Many Sustainable Technology Applications
Biodegradable electronics can be used in a range of sustainable technologies, such as solar cells or energy storage devices. For example, researchers are developing biodegradable solar cells made from organic materials that can be broken down safely in the environment. These technologies have the potential to provide clean energy solutions without contributing to electronic waste.
Biodegradable Electronics Reduce Hazardous Materials
Traditional electronic devices often contain hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, or cadmium, which can be harmful to the environment and human health. Biodegradable electronics, however, are made from materials that are safe for the environment and do not contain these hazardous substances.
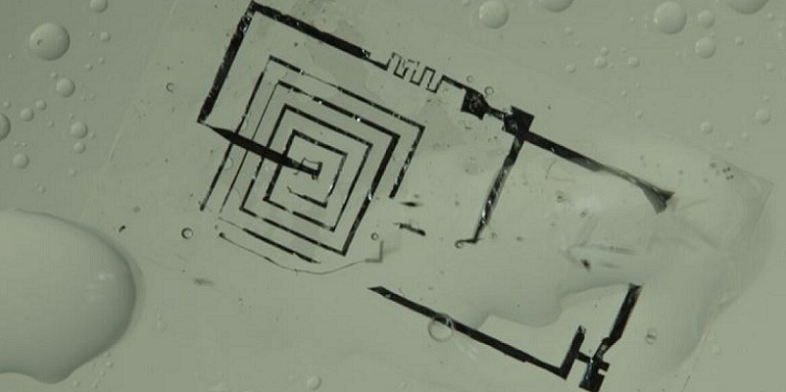
Challenges and Limitations of Biodegradable Electronics
While biodegradable electronics offer many environmental benefits, there are also several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed in their development.
- Durability and reliability: Biodegradable materials may not be as durable or reliable as traditional electronic materials. This is because biodegradable materials are designed to break down over time, which can lead to a shorter lifespan for electronic devices. For example, biodegradable electronics may be less resistant to moisture or temperature fluctuations, which can affect their performance and reliability.
- Cost: Biodegradable materials can be more expensive than traditional electronic materials, which can make biodegradable electronics more expensive to produce. This can limit their use in certain applications, such as consumer electronics, where cost is a significant factor.
- Regulatory hurdles: Biodegradable electronics may face regulatory hurdles due to safety concerns or lack of established standards. For example, the safety and biocompatibility of biodegradable materials need to be established before they can be used in medical devices or implants. There may not be established standards for the disposal or recycling of biodegradable electronics, which can make it difficult to ensure their safe and proper disposal.
- Limited applications: Biodegradable electronics may have limited applications due to their durability and reliability limitations. For example, they may not be suitable for use in high-performance electronic devices, such as smartphones or computers, which require high durability and reliability.
- Limited availability: Biodegradable electronics are still in the early stages of development, and there are only a limited number of companies and research groups working on their development. This limited availability can make it difficult for companies and consumers to access biodegradable electronics.
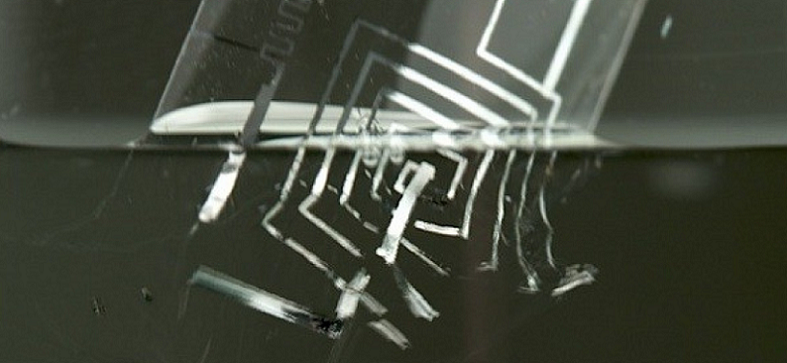
Future Outlook of Biodegradable Electronics
Biodegradable electronics have a promising future ahead as researchers and companies continue to explore new materials and technologies to create these devices. They have the potential to revolutionize various fields and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Biodegradable electronics can be used in medical implants, such as sensors and drug delivery systems that can be safely absorbed by the body. They can also be used in environmental monitoring devices to collect data and reduce the need for manual collection and disposal.
Biodegradable materials can be used to create sustainable consumer electronics and energy storage devices. Wearable sensors made from biodegradable materials can be used in fitness trackers or medical monitoring devices.
However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed, such as improving the durability and reliability of biodegradable materials, reducing production costs, and establishing regulatory standards for their use and disposal. With continued research and development, biodegradable electronics can become a viable alternative to traditional electronics and help reduce electronic waste while promoting environmental sustainability.
