As technology continues to evolve, touch screens have become the standard interface for many devices. However, touch screens are limited in their ability to convey rich sensory information. This is where haptic technology comes in, offering the potential for more immersive and engaging experiences.
What is Haptic Technology?
Haptic technology, also known as tactile feedback technology, is a type of technology that recreates the sense of touch through vibrations, force, and other sensations. Haptic technology enables users to interact with digital interfaces by feeling and sensing objects in a virtual environment, allowing for a more immersive experience.
The technology is based on the concept of haptics, which is the study of how people touch and feel things. Haptic technology involves the use of devices such as motors, sensors, and actuators to simulate the sense of touch. When a user interacts with a haptic device, the device provides feedback through vibrations, force, or other tactile sensations, allowing the user to feel the object or environment being simulated.
Haptic technology can be divided into two main categories: tactile feedback and force feedback. Tactile feedback is the use of vibrations or other tactile sensations to create the feeling of touching an object. Force feedback, on the other hand, involves the use of actuators to simulate the feeling of resistance or pressure, creating the sensation of lifting or pushing an object.
There are many different types of haptic devices, including haptic gloves, haptic vests, haptic chairs, and even haptic shoes. Haptic technology is also integrated into many consumer devices, such as smartphones and gaming controllers, to provide a more immersive experience for users.
The development of haptic technology has been driven by the desire to create more realistic and engaging virtual environments for users. Haptic technology has a wide range of applications, including medical and rehabilitation, gaming, education and training, and even remote control of machinery and robotics.

Applications of Haptic Technology
Haptic technology has a wide range of applications across various industries, including medical and rehabilitation, gaming, education and training, and remote control of machinery and robotics.
Haptic Technology in Medicine and Rehabilitation
Haptic technology has significant potential in the medical field. It can be used to simulate surgical procedures, allowing doctors and medical students to practice and refine their skills in a safe and controlled environment. Haptic technology is also being used in rehabilitation to help patients regain mobility and improve their motor skills.
Haptic Technology and Gaming
Haptic technology has been integrated into many gaming devices, such as controllers and virtual reality headsets, to provide a more immersive gaming experience. The technology allows players to feel the physical impact of in-game events, such as gunfire or collisions, adding an extra level of realism to gameplay.
Using Haptic Technology in Education and Training
Haptic technology has significant potential in education and training. It can be used to simulate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice and develop their skills in a safe and controlled environment. For example, haptic technology can be used to simulate a surgical procedure or a flight simulator, allowing learners to develop their skills before entering the real world.
Haptic Technology for Remote Control of Machinery and Robotics
Haptic technology can be used to control machinery and robotics remotely. The technology allows operators to feel the movements and actions of the machinery or robot, making it easier to control and perform complex tasks.
Haptic Technology Enhances Accessibility
Haptic technology can be used to enhance accessibility for people with visual or hearing impairments. For example, haptic feedback can be used to help blind or visually impaired users navigate digital interfaces or read braille, while haptic feedback combined with audio can be used to enhance the experience for users with hearing impairments.
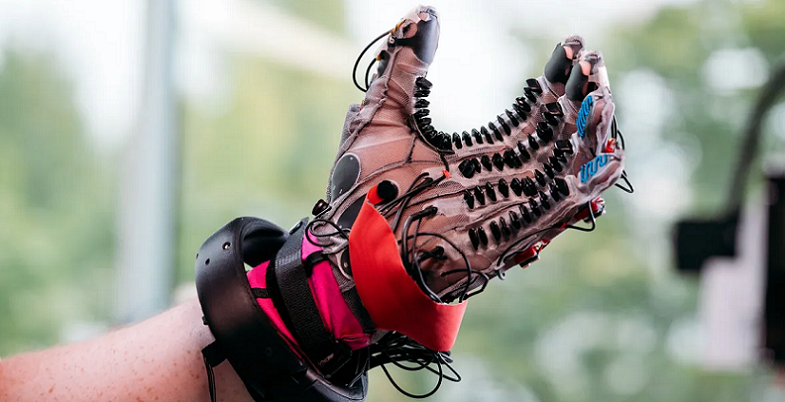

Future of Haptic Technology
The future of haptic technology is very promising, with the potential for significant advancements and new applications.
Haptic Technology Can Enhanced Sensory Feedback
One of the main areas of focus for the future of haptic technology is enhanced sensory feedback. Researchers are working to develop new types of sensors and actuators that can provide more detailed and realistic feedback to users. This could include the ability to simulate different textures, temperatures, and even smells.
Haptic Technology Will Improve Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Haptic technology has already been integrated into virtual reality and augmented reality devices, but there is potential for even more immersive experiences. For example, haptic technology could be used to simulate the feeling of walking on different surfaces or interacting with objects in a virtual environment.
Medical Applications Will Make Use of Haptic Technology
Haptic technology has significant potential in the medical field, and there is ongoing research into its applications for surgery and rehabilitation. In the future, we may see the development of more advanced haptic devices that can simulate the feeling of different types of tissue, allowing for more realistic surgical simulations.
Wearable Devices Will Incorporate Haptic Technology
As the technology continues to advance, we may see the development of haptic devices that can be worn on the body. This could include haptic clothing or accessories that can provide feedback to users based on their movements or interactions with the environment.
Haptic Technology Can Improve Communication and Human Connection
Haptic technology has the potential to enhance communication and human connection by allowing people to interact with each other in new ways. For example, haptic technology could be used to simulate the feeling of a hug or a handshake, allowing people to feel connected even when they are physically apart.
Ethics and Haptic Technology
Haptic technology, like any other technology, raises ethical considerations that must be taken into account. There are several important ethical considerations related to haptic technology that are important to understand.
One key consideration is safety. Haptic technology involves the use of vibrations, force, and other tactile sensations to simulate the feeling of touch. If these sensations are too strong or used improperly, they could potentially cause harm to users. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that haptic devices are designed and used safely, with appropriate safeguards in place to prevent harm to users.
Another ethical consideration related to haptic technology is privacy. Haptic technology may involve the collection and use of sensitive data, such as biometric information. It is essential to ensure that users are informed about how their data is being collected and used and that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect their privacy.
Accessibility is another significant ethical consideration related to haptic technology. While haptic technology has the potential to enhance accessibility for people with disabilities, it is important to ensure that the technology is designed in a way that is inclusive and accessible to all users. This may include considerations such as designing devices that are easy to use and providing appropriate support and training.
Equity is also a crucial ethical consideration related to haptic technology. As with any technology, there is a risk that haptic technology could exacerbate existing inequalities if it is not designed and deployed in an equitable way. It is important to consider how the technology can be used to promote equity and ensure that it is accessible to all users, regardless of their background or circumstances.
As haptic technology continues to evolve and become more widespread, there may be a need for regulation to ensure that it is used safely and ethically. This may include regulations around the design and use of haptic devices, as well as regulations around the collection and use of user data.
