
In today’s fast-paced world, we’re constantly bombarded with stimuli, from the blaring of car horns to the endless scrolling through social media feeds. This overstimulation can have negative effects on our mental health, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and even depression. That’s where float therapy comes in. By immersing oneself in a tank filled with highly buoyant saltwater, float therapy provides a unique environment of sensory deprivation, allowing the mind to relax and reset.
What Is Float Therapy?
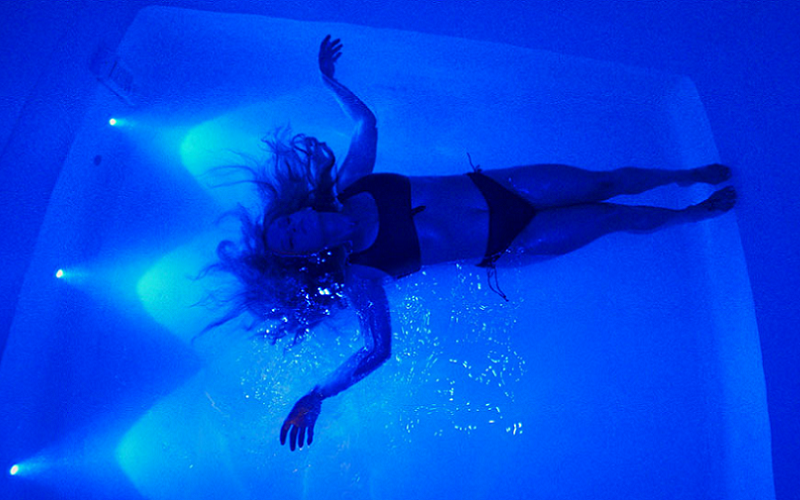
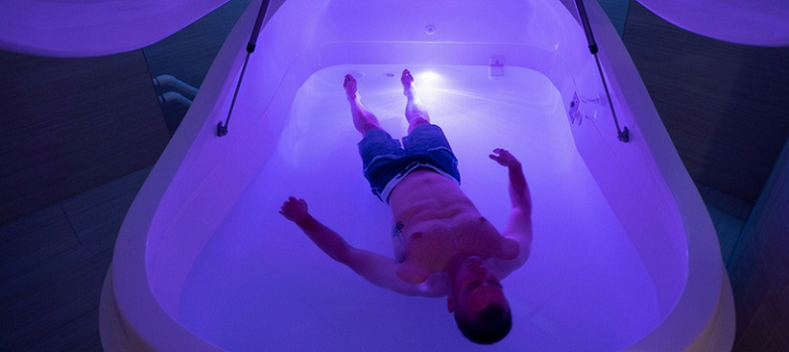
Float therapy, also known as floatation therapy or sensory deprivation, is a type of alternative therapy that involves immersing oneself in a tank filled with highly buoyant saltwater, typically heated to body temperature. The tank is often referred to as a “float tank,” “isolation tank,” or “sensory deprivation tank.” The tank is designed to minimize external stimuli such as sound, light, and temperature, creating an environment of sensory deprivation.
The saltwater in the tank is infused with a high concentration of Epsom salt, which makes the water denser than regular water, allowing the body to float effortlessly. This weightlessness, combined with the lack of external stimuli, creates a unique environment for the mind and body to relax and recharge.
Float therapy was first developed in the 1950s by John C. Lilly, a neuroscientist who was interested in the effects of sensory deprivation on the brain. Since then, float therapy has gained popularity as an alternative therapy for a wide range of physical and mental health conditions. The isolation invokes feelings similar to how nature therapy can promote healing.
The experience of float therapy typically lasts for 60 to 90 minutes, with the individual floating in the tank in complete darkness and silence. The tank is designed to be completely soundproof and lightproof, with the temperature of the water and air inside the tank set to match the temperature of the body, making the individual feel weightless and completely comfortable.
During the float session, the brain experiences a decrease in sensory input, allowing it to enter a deep state of relaxation. This relaxation can have numerous benefits, including stress reduction, improved sleep quality, and relief from symptoms of anxiety and depression. The weightlessness of the body can help to relieve joint pain and muscle tension, making it an effective therapy for individuals with chronic pain conditions.

The Science Behind Float Therapy
The science behind float therapy involves the principles of sensory deprivation and the relaxation response. When a person enters a float tank, they are removing themselves from the normal sensory input they receive from the environment.
This lack of sensory input is the principle behind sensory deprivation. The body and mind are no longer processing the sensory information they normally receive from the external environment, allowing the mind to enter a state of relaxation and potentially accessing a deeper state of consciousness.
During a float therapy session, the brain enters a state of relaxation through the release of endorphins and the reduction of stress hormones such as cortisol. Endorphins are natural chemicals that the body produces, which can help to reduce pain and create feelings of happiness and euphoria.
These endorphins are released during a float session, providing a sense of relaxation and well-being. The reduction in cortisol levels, which are associated with stress, also contributes to the relaxation response that is often experienced during a float therapy session.
The brain waves of a person in a float tank shift from the beta state, which is associated with the active mind, to the alpha and theta states, which are associated with relaxation, creativity, and a deeper state of consciousness. These brain wave states are similar to those achieved during meditation, and can lead to a sense of calm and increased mental clarity.
The weightlessness of the body during a float session can have physical benefits. The reduction in gravitational pressure on the joints and muscles can help to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, making float therapy a popular option for individuals with chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and arthritis.
Research has shown that float therapy can have numerous benefits for mental and physical health. Studies have found that float therapy can reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and PTSD. It has also been shown to improve sleep quality and cognitive function. The physical benefits of float therapy include reducing muscle tension and inflammation, improving circulation, and boosting the immune system.
The Mental Health Benefits of Float Therapy
Float therapy can provide several benefits for mental health. It offers a unique environment that allows the mind and body to relax and recharge. During float therapy, the brain produces less cortisol, a hormone associated with stress, and releases more endorphins, which promote feelings of relaxation and well-being. This relaxation response can lead to a reduction in feelings of anxiety and stress.
The sensory deprivation and weightlessness of float therapy allow the mind and body to enter a state of deep relaxation, leading to increased mindfulness and improved mood. Float therapy has also been shown to improve sleep quality by increasing the production of delta waves, which are associated with deep sleep.
Float therapy has been found to alleviate symptoms of depression by improving mood and reducing feelings of sadness and hopelessness. Float therapy can boost creativity and mental clarity by improving focus and problem-solving abilities.

Other Physical Benefits of Float Therapy
Float therapy can also provide physical health benefits. One such benefit is relief from chronic pain. The weightlessness of the body during a float session can help to relieve joint pain and muscle tension. This can also reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for individuals with chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and arthritis.
Float therapy has been shown to improve athletic performance by reducing muscle tension and soreness. Athletes can benefit from the deep relaxation and increased circulation that occur during a float session, which can help speed up recovery time after exercise.
Float therapy can boost the immune system. Studies have shown that float therapy can increase the production of white blood cells, which help to fight off infections and diseases. The deep relaxation and stress-reducing effects of float therapy can also contribute to a stronger immune system.
Who Can Benefit from Float Therapy?
Float therapy can benefit a wide range of individuals seeking to improve their overall well-being. Specifically, people with anxiety disorders can benefit from float therapy’s ability to reduce stress and anxiety.
Individuals with chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and arthritis can benefit from the pain relief provided by float therapy. Athletes can benefit from float therapy’s ability to reduce muscle tension and soreness, which can improve athletic performance.
Creatives can benefit from float therapy’s ability to boost mental clarity and creativity. Anyone seeking relaxation and mindfulness can benefit from float therapy’s unique environment of sensory deprivation and weightlessness.
What to Expect during a Float Therapy Session
If you’re considering trying float therapy, here’s what you can expect during a typical float therapy session:
- Preparation for a session: Before entering the float tank, you will need to shower to remove any oils or products from your skin or hair. This helps to ensure that the water in the tank stays clean and sanitary. You may also be provided with earplugs to help block out any sound.
- The experience of floating: Once you enter the tank, you will float effortlessly in highly buoyant saltwater, with the water heated to match the temperature of your body. The tank will be dark and soundproof, with no external stimuli. You can choose to keep the tank lid open or closed, depending on your level of comfort.
- Aftercare and tips for making the most of the experience: After your float session, you will shower again to remove any saltwater from your skin and hair. You may also be provided with a post-float area to relax in, with water or tea available to help you rehydrate. Take your time getting up and moving around after your float, as your muscles may be very relaxed.
Here are some additional tips to help you make the most of your float therapy experience:
- Relax and let go: Try to relax as much as possible during your float session. Let go of any thoughts or worries and simply focus on the feeling of weightlessness and relaxation.
- Use breathing techniques: Focusing on your breath can help to deepen your relaxation and mindfulness during the float session.
- Experiment with music or guided meditations: Some float therapy facilities offer the option of playing music or guided meditations during the float session. You can experiment with these options to see if they enhance your experience.
- Be patient: It may take a few float sessions to fully acclimate to the experience and fully relax. Be patient with yourself and allow yourself time to adjust to the unique environment.
